Industry Analysis Report on the Development of Stem Cell Therapy Industry in China in 2017
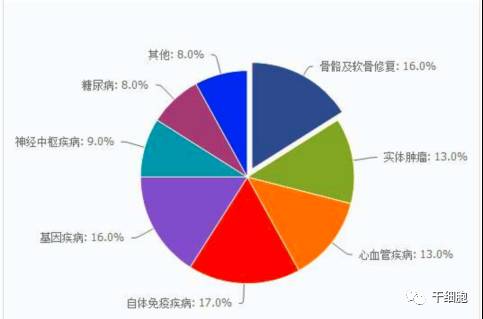
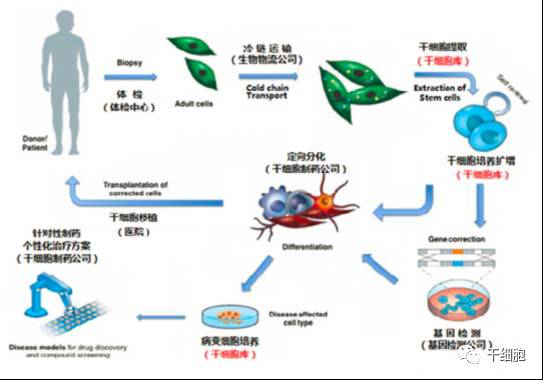
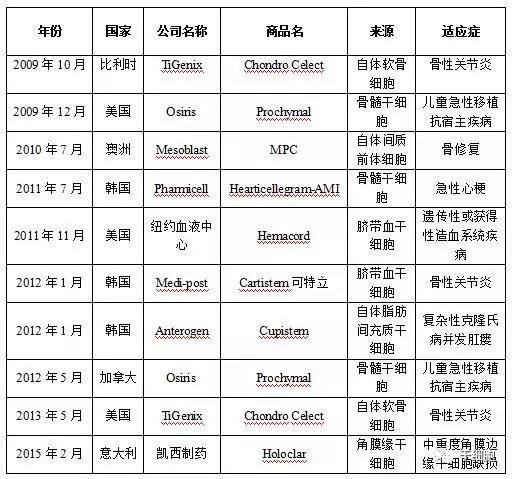
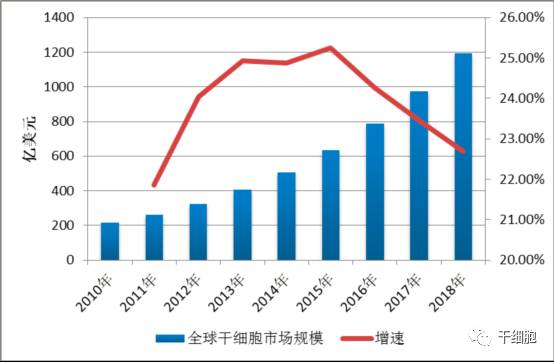
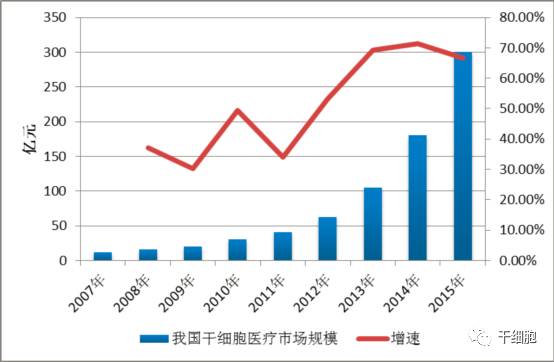
Source: China Net Guolian Securities Jiang Yimin July 24, 2017 I. Industry Overview (1) Basic overview of the industry Stem cells are a kind of pluripotent cells with self-replication ability and multi-directional differentiation potential. They are the seed cells of the human body and are called "universal cells" by the medical community. Stem cells and their differentiated products provide a new way to effectively repair important tissues and organs of the human body and to cure cardiovascular diseases, metabolic diseases, nervous system diseases, blood system diseases, autoimmune diseases and other important diseases, with stem cell therapy as the core. Regenerative medicine will become the treatment of another disease after drug treatment and surgery, thus establishing the core of the new medical revolution. "Trafficking Therapy Indications Map", Data Source: Wind Information On February 9, 2006, the State Council pointed out: "In the next 15 years, to improve the quality of the population and the health of the whole people, there is an urgent need for strong support from science and technology." The development idea is: "The focus of disease prevention and control is shifted forward, and prevention is the main focus. Combining health and disease prevention and research, researching key technologies for prevention and early diagnosis, and significantly improving the ability to diagnose and prevent major diseases. This is the first time that China has written stem cell research technology as a key technology field into the national major science and technology strategic development plan. From 2007 to 2012, China basically pursued the supervision idea that “stem cells are medical means rather than drugsâ€. Under this guiding ideology, due to the huge profits of the stem cell industry, more than 62% of Grade A hospitals in the country (including military regions) The hospitals have carried out different levels of stem cell therapy business "with the qualification of medical units". Even many medical and scientific personnel from abroad have come to China for stem cell research. Some overseas tour groups have even used "stem cell tourism" advertisements to allow foreign citizens to enter China for stem cell treatment, which has caused "stem cells are drugs, and they need to pass careful experiments." Strictly supervised" is the condemnation of Western developed countries that are dominant. On January 10, 2012, due to the urgency of the domestic regulations on stem cells and the pressure of the International Health Organization, the Ministry of Health stopped all stem cell treatment activities in mainland China. Since then, China's stem cell industry has finally officially entered national regulations. Under the supervision. On March 7, 2013, the Ministry of Health/National Food and Drug Administration jointly issued the "Cell Cell Clinical Trial Research Management Office (Trial)", "Cell Cell Clinical Trial Research Base Management Measures (Trial)" and "Stem Cell Preparation Quality Control and Preclinical Research Guidelines (Trial), which regulates the research and application of stem cells in China. According to these three regulations, the stem cell industry will form: “stem cell bank (drugs) → stem cell preparation companies (pharmaceutical plants) → medical service institutions (hospitals)†This industrial chain, in which the stem cell bank has become the foundation and core of the entire industry. Under the government's strong investment and the continuous breakthrough of innovation by researchers, China's stem cell industry has been in the leading position in the second echelon after developed countries in Europe and America. On February 26, 2015, after two years of repeated discussions with experts from the government, domestic biomedicine, clinical medicine, and law, the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China promulgated the National Key Research and Development Program for Stem Cell and Translational Medicine. (Consultation draft). The programme identifies the overall goals and main tasks in the field of stem cell research from 2015 to 2020. For the first time, stem cell research is clearly defined in the national key scientific research task. On July 20 of the same year, the National Health and Family Planning Commission and the State Food and Drug Administration issued the "Measures for the Management of Stem Cell Clinical Research (Trial)". This method is the first time in the past three years since the domestic stoppage of stem cell therapy in 2012, the first pre-standardization of stem cell clinical treatment has been published in detail in the form of national regulations through the eight chapters and 55 rules. This also directly means that the era of comprehensive and orderly stem cell clinical treatment in China has been opened. Throughout the development of China's stem cell technology and industry over the past decade, we can clearly see a trajectory from non-complete norm to full norm, from vague to clear, industrial development from weak to strong, and government support continues to rise. (II) Status quo of industry development From the perspective of the global market, stem cell technology and development have been popular in the international capital market in recent years. In the listed stocks listed on NASDAQ, the market value of stem cell concept stocks exceeds 30 billion US dollars. Sansheng's “2014-2018 China Stem Cell Market Panorama Survey and Development Trend Forecast Analysis Report†predicts that the global stem cell industry's potential market in the past two years will be about 80 billion US dollars, and up to 400 billion US dollars by 2020. According to the research report of the first startup, under the national policy and capital promotion, the Chinese stem cell industry has formed a complete industrial chain from upstream storage to downstream clinical applications. It is expected that the stem cell industry revenue will increase from the current 2 billion in the next 5 years. To 30 billion, the average annual growth rate is 170%. From the collection of human waste samples carrying stem cells, to the extraction and expansion of stem cells, to the storage of stem cells until stem cell applications, the stem cell industry chain has a high profit margin in all links and has good profitability. Source: wind information According to the "2014-1919 China Stem Cell Medical Industry Market Analysis and Investment Prospects Forecast Report", China's current industrial application of stem cells is mainly in stem cell storage, cell preparation, research technology, therapeutic solutions and related basic services. In the field of stem cell research, there are many institutions and enterprises, but most of them are still in the exploratory stage; the Zhongyuan Concord, which has already been listed, and the North Branch, which has acquired venture capital, have opened up space in this field. In the field of stem cell therapy, the number of hospitals entering the field of stem cell therapy every year has reached dozens, and many professional hospitals are also actively pursuing new methods and techniques for stem cell therapy. In addition, China has established a number of industrial bases, including the National Stem Cell Industrialization East China Base, the National Stem Cell Industrialization Tianjin Base, the Qingdao Stem Cell Industrialization Base, the Wuxi International Stem Cell Joint Research Center, and the Taizhou National Bio-Industry Base Stem Cell Industrialization Project Base. Wait. At the end of 2010, the establishment of a strategic alliance for technological innovation in the national stem cell and regenerative medicine industry promoted innovation, transformation of results and industrial development of stem cell and regenerative medicine technologies. (3) Relevance between upstream and downstream industries The stem cell industry upstream is the stem cell collection and storage business. The main models are the collection and storage of cord blood stem cells, umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, placental hematopoietic stem cells, placental sub-total stem cells, placental mesenchymal stem cells, adipose stem cells, menstrual blood, etc.; Mainly to develop stem cell preparations, stem cell new drugs, stem cell medical technology applications, etc., thus forming a large industrial chain. 1. Upstream analysis of the industrial chain The upstream of the stem cell collection and storage industry includes biological agents, biological laboratory consumables and equipment. The biological reagent industry mainly provides preservation liquid, digestive enzyme, culture medium, cryopreservation reagent, etc. for stem cell collection and storage. The biological experiment consumables provide test consumables such as disposable sterile culture dishes/bottles and centrifuge tubes. Biological laboratory equipment provides instrumentation equipment for stem cell detection and preparation. Due to the abundant product and abundant supply of stem cell collection and storage, there is no restriction on the company's development. 2. Downstream analysis of the industry chain The downstream mainly focuses on the development of stem cell preparations, stem cell new drugs, and stem cell medical technology applications. Stem cell products include stem cell drugs, stem cell transplantation technology, stem cell beauty and anti-aging technology, as well as seed cells in tissue engineering, gene therapy cell carriers, stem cell-based drug screening models, etc. With the development of biotechnology, stem cell applications The field will continue to expand. At present, there are nearly 10 kinds of stem cell products on the market, and most of them are in the research stage. There are no forms of drugs listed in China. There are three types that have been approved by two countries, such as ChondroCelect stem cell drugs developed by TiGenix in Belgium. They passed the European EMA approval in 2009 and passed the US FDA approval in 2013. The Prochymal stem cell drug developed by Osiris in the United States was approved by the US FDA in 2009, and passed the Canadian HC approval in 2012. Cartistem, a South Korean company developed by Medi-post, passed the FDA review in South Korea in 2012 and the US FDA in 2013. The details are as follows: (4) Industry market scale According to research data from international research institutions Market Research and Transparency Market Research, the global stem cell market is about 21.5 billion US dollars in 2010, and has exceeded 40 billion US dollars by 2013. It is expected that by 2018, the potential market size of global stem cell medical treatment will reach $119.5 billion. In terms of market distribution, North America and Western Europe are still the largest stem cell markets, accounting for 44% and 38% respectively, while Asia Pacific ranks third, accounting for 17% of the market. Source: Market Research, Transparency Market Research According to the research report of Huabao Securities Research Institute, China's stem cell industry revenue in 2009 was about 2 billion yuan. In 2012, China's stem cell market reached 6.2 billion yuan. With the market of stem cell treatment expanding, China's stem cell industry in 2014. The scale reached 18 billion, and according to the forecast at that time, it will reach 30 billion yuan by 2015, with a compound growth rate of more than 50%. Source: Warburg Securities Research Institute (5) Regional, cyclical and seasonal characteristics of the industry Stem cell therapy is mainly for nervous system diseases, cardiovascular diseases, liver diseases, kidney diseases, blood diseases, diabetes, and the occurrence of such diseases has no obvious periodic and seasonal characteristics. Stem cell therapy technology is at the forefront of current biomedical technology, and has high requirements for R&D team and equipment, and the corresponding stem cell extraction, storage and follow-up treatment are expensive. It is widely used in economically developed first- and second-tier cities, so stem cell extraction It has a certain regionality with the distribution of storage services. Second, the main barriers to enter the industry (1) Technical barriers The stem cell industry is an emerging industry that is knowledge-intensive, technology-intensive, and highly integrated across disciplines. The research and development and application of stem cell-related products have high technical content, especially in the field of research and development of new stem cell drugs and the establishment of cell models. It requires cross-disciplinary and high-level talents such as molecular biology, clinical medicine, pharmacy, bioengineering, and quality management engineering. Professional cooperation can guarantee the smooth development of the project. International companies engaged in stem cell services mainly carry out research and development and industrialization of stem cell technology through project cooperation research and development, relying on research institutes or universities to jointly build laboratories. The introduction of China's industry laws and regulations has strengthened the standardized management of stem cell technology research. Therefore, the industry has high technical barriers. (2) Talent barriers The stem cell industry is a typical high barrier industry. The talent team determines the development space of the enterprise, especially the industry leaders are crucial to the development of the industry. The high-quality talents with compound professional knowledge structure and R&D application ability are the core resources. For the new entrants of the stem cell industry, it is very difficult to gather and construct a professionally qualified talent team in a short period of time, and employ industry authority as the chief scientist. In the absence of benefits, it is also difficult to ensure the stable development of the talent team. Therefore, there are obvious talent barriers in the stem cell industry. (3) Financial barriers The stem cell industry is an emerging industry, and the industry is in its infancy. Therefore, many of them stay in the laboratory research and development stage, and have not formed scale effects. They are high-input, low-output industries. Many domestic enterprises have begun to enter the research and development stage of stem cell drugs. They are all in preclinical research. They need to invest a lot of manpower, material resources and financial resources. Once they enter clinical research, the capital investment will increase substantially. At the same time, it is necessary to build a new production and production workshop and pass GMP certification. . Important instruments and equipment are basically imported, and are special custom non-standard equipment, which is expensive. In the later stage of construction and sales network, it is also necessary to invest funds. If a new product wants to occupy the market in a short period of time, it needs to invest huge amounts of money in the process of marketing and sales team construction. Therefore, a large amount of capital demand has increased the threshold for entry into the stem cell industry. (4) Regulatory barriers As a cross-disciplinary discipline of life sciences and regenerative medicine, the stem cell industry's research and development conditions, management and application of research and development results are all under the strict supervision of the state. Therefore, the state has enacted a series of laws and regulations in terms of industry access, clinical research, and technical applications, and strictly supervises the effectiveness and safety of stem cell technology and products. 3. Favorable and unfavorable factors affecting the development of the industry and industry risk characteristics (1) Favorable factors affecting the development of the industry 1. Support for national industrial policies China attaches great importance to stem cell technology. At the beginning of 2006, the State Council clearly stated in the National Medium- and Long-Term Plan for Science and Technology Development (2006-2020) that it should vigorously develop biotechnology and include "human cell tissue engineering technology based on stem cells" in biology. The frontier of technology. In 2010, the State Council issued the "Decision of the State Council on Accelerating the Cultivation and Development of Strategic Emerging Industries", including the "bio-industry" in the rapid development of key areas, and promoting the development, demonstration and application of key technologies for bio-manufacturing. Stem cells belong to this category. During the “Eleventh Five-Year Plan†period, the stem cell industry received strong support from the national “973 Programâ€, “863 Program†and “National Major Scientific Research Program for Development and Reproduction Researchâ€. In 2012, the Ministry of Science and Technology released the “12th Five-Year Plan†for the National Major Scientific Research Program for Stem Cell Research, which listed nano-research, quantum-regulation research, protein research, development and reproduction research, stem cell research, and global change research as six major countries. The special plan for the scientific research plan "12th Five-Year Plan". In August 2016, the State Council officially issued the “13th Five-Year National Science and Technology Innovation Planâ€. Stem cells and regenerative medicine, as a new biomedical technology, are emphasized to have innovative breakthroughs and application development to promote technology transformation and application and serve the country's economic and social development, and greatly enhance the international competitiveness of the bio-economy. In October 2016, the Ministry of Science and Technology issued the “Notice on the Issuance of the Key Projects for 2017 Annual Projects of Stem Cell and Transformation Research of National Key R&D Programsâ€. The “Stem Cell and Transformation Research†pilot project was again focused on the 2016 key special projects. One of the special projects is required to fully deploy research tasks from eight aspects including stem cell clinical research and stem cell resource library, and strive to promote the transformation of stem cell research results into clinical applications, and to improve the overall technical level of stem cells and translational medicine in China. In October 2016, the "Healthy China 2030" Planning Outline issued by the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council was published in full. The plan outlines that by 2030, China's main health indicators will enter the ranks of high-income countries, among which "stem cells and regenerative medicine" as major technologies. The project was included in the planning outline to promote medical science and technology advancement and promote health science and technology innovation. In December 2016, the State Council officially issued the “13th Five-Year Plan for the Development of Strategic Emerging Industries in the Countryâ€, and made comprehensive arrangements for the development goals, key tasks, and policy measures of China's strategic emerging industries during the 13th Five-Year Plan period. By 2020, the scale of the bio-industry will reach 8-10 trillion yuan. In January 2017, the National Development and Reform Commission issued the “13th Five-Year Plan for Biological Industry Development†focusing on the biotechnology industry. In February, the National Development and Reform Commission released the “Guidelines for Key Products and Services for Strategic Emerging Industries†to support cells including stem cells. The development of bio-industries in the fields of therapeutic products. 2. Industry development tends to be standardized Before 2011, the stem cell field developed rapidly, but due to lack of regulation and supervision, the industry development was more chaotic. In order to promote the standardized operation and healthy development of the stem cell industry, the former Ministry of Health and the State Food and Drug Administration launched a one-year clinical research and application standard rectification work in 2011. At the end of 2011, the “Notice on Conducting Stem Cell Clinical Research and Application Self-examination and Self-correction Work†was issued, requesting the rectification of the ongoing clinical application of stem cells. In 2015, the State Health Planning Commission and the General Administration of Food and Drug Administration promulgated the "Cell Cell Clinical Research Management Measures (Trial)" and "Stem Cell Preparation Quality Control and Preclinical Research Guidelines (Trial)". These two major policies mean the Chinese stem cell industry. Formally have clear laws and regulations, aiming to regulate the behavior of stem cell clinical research, protect the rights and interests of subjects, promote the healthy development of stem cell research, and lay a good policy foundation for the standardized development of stem cell industry. In December 2016, the State Food and Drug Administration issued the "Guidelines for the Research and Evaluation of Cellular Products (Draft for Comment)", which first included stem cells in drug management, and clarified that enterprises can carry out preclinical and in accordance with the requirements of the State Food and Drug Administration. Clinical trials, and report to the State Food and Drug Administration the IND clinical approval, NDA new drug certificate and production approval. (2) Unfavorable factors affecting the development of the industry 1. The regulatory system needs to be improved At present, the regulatory documents for stem cell research, clinical application and product development are mainly based on methods, guidelines and principles. They have not risen to the legislative stage and lack operability. Due to insufficient legal supervision, industry standards are not clear and restrict the development of the industry. 2. Insufficient technical innovation capability The development of stem cell industry in China is mainly based on stem cell collection and storage. Lack of enterprises with core technologies and talents lacks product and technology innovation capabilities, which is not conducive to communication and development within and outside the industry. Foreign technology is gradually maturing, while the development of stem cell industrialization in China is lagging behind, and the ability to transform innovation results is insufficient. As foreign companies with strong R&D capabilities and technologies accelerate their inflow into China, the impact on domestic enterprise development is inevitable. 3. Insufficient capital investment At present, China's stem cell research funds mainly come from government or social sponsorship, and enterprise development is obviously subject to insufficient funds. Although domestic social capital and VC/PE are generally optimistic about the development of the stem cell industry, due to the long period of investment, the investment in the stem cell industry is limited, which restricts the development of the stem cell industry. (3) Basic risk characteristics of the industry 1. Risks of inadequate industry regulatory policies China's stem cell field supporting regulations are still in the process of continuous improvement. Can we establish, improve and refine China's management regulations on stem cell research and application as soon as possible, so that it is clear, effective, standardized and enforceable, which will result in the company's continuous operation. influences. The source of human embryonic stem cells involves moral and ethical constraints. The United States, as a country where cell biotechnology started earlier, has once suspended stem cell technology research because of ethical controversy. Therefore, due to the lag, conservative and ethical constraints of legal policies, the development of stem cell technology has certain uncertainties, and the imperfection of industry regulatory policies brings certain risks to the company's ability to continue operations. 2. Product development risk Cell therapy is a cutting-edge technology in the field of international biotechnology. The cell technology mastered by the company has reached an advanced level in terms of technical content, research and development and industrialization level, but the specific research and development projects still have objective risks that the research and development results do not achieve the expected results. Since R&D and applied research in the field of cell therapy require solid technology, talents, and financial support, such as failure of technology research and development, or technical achievements cannot be smoothly converted into industrial applications, the company will face greater losses. 3. Risk of medical disputes As a new type of treatment, cell therapy technology has the irreplaceable advantages of traditional methods, but it still faces the risk of medical disputes. Because cell technology is a cutting-edge technology in the biological sciences, and patients' physiques and diseases are different, cell therapy does not rule out the consequences of poor treatment or side effects, and the medical disputes that may arise are also the risks faced by biotech companies. one. 4. Risk of brain drain Technicians are one of the important driving forces for the company's sustainable development. As a high-tech biotechnology company, the company's professional and technical personnel play an important role in the company's technological development and innovation. Although the company has adopted a series of measures to stabilize the technical staff and achieved good results, it still cannot rule out the possibility of loss of technicians. If the company loses its technicians, it will have a negative impact on technology research and development and sustainable development. 5. Intellectual property risk At present, China's intellectual property rights related laws and regulations need to be further improved, and the status quo of public intellectual property rights is not strong, leading to the issue of intellectual property protection has always been a difficult problem in various domestic industries. As a high-tech biotechnology company, although the company protects the company's self-developed patent technology by applying for technology patents, it does not rule out the possibility that direct competitors steal the company's core technology and adversely affect the company's operations. At present, China has adopted a series of specific measures to increase the protection of intellectual property rights, but the implementation of these measures needs to be improved. The company will still face the risk of intellectual property protection for a period of time. 6. Market competition increases risk With the continuous development of the stem cell industry, the industry competition has intensified to promote the trend of upstream and downstream enterprises covering the entire industrial chain. The upstream company extended to the downstream industry, increased research and development of stem cell clinical research and medical technology; downstream R&D and treatment institutions infiltrated the upstream industry, and established their own stem cell banks, whether the company can successfully establish itself in the future industrial chain integration process. The brand's share of market share will have a direct impact on the company's business prospects. Reprinted from the public number "Stem Cell" Gummy Candy,Gummy Worms,Sweet Candy,Soft Candy Montreal Shantou Food Co., Ltd , https://www.montrealsnack.com