Common pest and disease maps of grape growing, green blind cockroaches prevention methods and special effects drugs
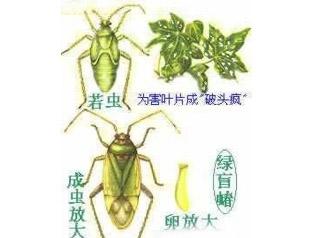
As the temperature rises, pests in the vineyards begin to take place, and from today we will be able to explain the pests in the vineyard in a few stages. Start with the most common green blinds. The green-streaked owl, also known as the flower-leaf worm, belongs to the genus Hemiptera. There are many host plants, which can damage many kinds of crops such as fruit trees, vegetables, cotton and alfalfa. It is an important pest on cotton. In recent years, with the adjustment of the agricultural industrial structure and the expansion of the grape planting area, the harm of the green blind mites on the grapes has become increasingly serious and has become one of the important pests on the grapes. (1) Distribution and harm The green blind mites are widely distributed and are common throughout the country. It is distributed abroad in Japan, Europe, and the United States. The green scorpion scorpion is a bud, sucking the young shoots, young leaves, flower buds and young fruit of the grape. The process of thorns secretes venom, and the process of sucking sucks the plant juice, causing necrosis or abnormal growth of the damaged parts. After the young leaves of the grapes are killed, the dead spots appear first, and the leaf buds expand, and the small dots become irregular polygonal holes, commonly known as "broken leaves"; after the flower buds are damaged, they stop developing, withered and shed; the early surface of the damaged young fruit It shows a small yellow-brown spot that is not obvious. As the fruit grows, the small spots gradually enlarge and appear black. The development of the damaged subcutaneous tissue is hindered and gradually sag, and cracks occur in severely damaged parts, which seriously affects the yield and quality of the grapes. Green blind cockroach hazard (leaf) Green blind mites (young fruit) (2) Morphological characteristics Eggs: about 1 mm long, yellow-green, squat pocket-shaped, egg-covered milk yellow, central depression, protruding at both ends, no appendages. Nymph: The nymph is 5 years old, green when first hatched, and compound eyes pink. The 5th instar nymphs are all bright green, the tentacles are pale yellow, the ends are darker, and the complex eyes are gray. The tip of the wing bud is blue, reaching the fourth section of the abdomen (color map 125). Adult: The body is about 5 mm long, and the female is slightly larger and green. The compound eyes are highlighted in black. The antennae are 4 filaments, shorter, about 2/3 of the body length, and the 2nd section is equal to the sum of 3 and 4 knots. The color is deeper toward the end, 1 section is yellow-green, and 4 sections are dark brown. The front chest plate is dark green with many black dots. The small scutellum has a triangular shape, yellow-green, and has a shallow vertical line in the center. The front wing diaphragm is translucent dark gray and green. Green blind (3) Life history and habits Three to five generations occur in one year, mainly in the egg bark in various fruit tree bark, between the buds, the dead branches, the cotton in the stems of the stems and the weeds or shallow soils. The wintering eggs began to hatch in March-April, and the hatching period of the wintering eggs was relatively neat. In late April, the grapes began to harm after germination. In the middle of May, the leaf-expansion period was the worst period, and the young fruit period began to be harmful in the middle and late May. Fruits, after the end of May, the temperature is getting higher and the insects are getting smaller. The first, second, third, and fourth generations appeared in early June, mid-July, mid-August, and mid-September. The overlapping phenomenon of the generations was serious, mainly shifting to crops such as beans, corn, and vegetables. Spawning winters from late September to early October. Adults have strong flying ability, and the nymphs are lively, lurking during the day, slightly disturbed, and quickly climbed, which is difficult to find during the day. It mainly sucks on buds, young leaves and young fruits in the early morning and evening. This is why you only see broken leaves and no insects. Adults have a long life span of about 30-40 days. They will lay eggs 6 to 7 days after emergence. The spawning period lasts for 20-30 days, and the spawning tends to be tender. It is prolific in young shoots, young leaves and flower buds. And young fruits and other tissues, but the wintering eggs are mostly produced in dead branches, hay and so on. (4) Occurrence and environment 1. The occurrence of climate-green scorpion mites is closely related to climatic conditions. It is warm and humid, and under high-humidity conditions, nymphs are active, growth is fast, and rainy years occur. The temperature is 20 to 30 ° C, and the relative humidity is 80% to 90%. In recent years, the temperature and humidity conditions in the middle and upper reaches of May are suitable, which is one of the main causes of serious occurrence of green blind mites. 2. The host is a green blind, but it has only been harmful in pasture and cotton. In recent years, with the adjustment of agricultural structure, especially since the large-scale promotion of transgenic cotton, the insects have been resistant to insects. The sex is better, the use of chemical pesticides in cotton fields is reduced, which is conducive to the occurrence and reproduction of green blind cockroaches. The number of insect sources has increased year by year, making it gradually become an important pest on various crops such as grapes, jujube trees, apples and vegetables. Planting cotton, pasture, jujube, legumes and other favorite plants in or around the vineyard provides favorable conditions for early spring food connection and nutrient supplementation, which is beneficial to its population. 3. Natural enemies, green blinds, and more natural enemies. Egg parasitic wasps are a little pulsed bee, blind black bee, and small bee. Predatory natural enemies include flower buds, grass mites, cockroaches, and spiders. It has a strong control effect under natural conditions. (5) Prevention methods Agricultural control (1) Clean up the flooding place. Before the wintering of the grapes (before the north is buried in the cold), the old rough skin on the branches is removed, and the egg cuts and dead branches are cut off. (2) Clear the cottonwood and cotton leaves in the cotton fields around the vineyard in time, remove the weeds under the trees and the fields, the ditch, the roadsides, and scrape the old skins of the surrounding fruit trees, and cut off the dead branches to destroy them. Reduce and cut off the source of the green blind cockroach overwintering insects and the early spring host. (3) During the growing period of the grapes, the weeds inside and outside the orchard are removed in time, and the summer shears and toppings are carried out in time to eliminate the latent nymphs and eggs. 2. Physical control One vibrating insecticidal lamp is hoisted every 4 hectares of orchard, and the phototaxis of the adult mites is used to trap and kill. 3. Chemical control (1) Unified prevention and control. The green blind cockroach has strong migration, and the effect of one household is not ideal. It is necessary to launch unified prevention and control according to the forecast and forecast. Townships (towns) and villages with conditions should set up a professional team for mechanical defense to achieve uniform time and uniform drug use. And unified action. (2) Appropriate timing of prevention. The green blind owl has a haunting habit, and the adult sneaks under the tree during the day, and the weeds in the ditch are mostly harmful at night and in the morning. Therefore, spray control should be carried out in the evening or early morning to achieve better control effects. (3) Pay attention to the protection and utilization of natural enemies. There are many natural enemies of the green blind cockroaches. When conducting chemical control, it is necessary to protect the natural enemies, and try to use neonicotinoid insecticides that are less toxic to natural enemies. (4) Before the early spring grape buds, the whole tree is sprayed with 3 waves of stone sulfur mixture to eliminate wintering eggs and newly hatched nymphs. After the wintering eggs hatch, grasp the nymphal stage of the wintering age and timely control the chemicals. Commonly used agents are: imidacloprid, acetamiprid, malathion, deltamethrin, beta-cypermethrin. Spray even 2 to 3 times, 7 to 10 days apart. Spraying must be meticulous and thoughtful, and spray the medicine on the trunk, the ground weeds and the inter-row crops, so that the trees and trees can be sprayed strictly and sprayed to achieve better control effects. "Niu Nongtang" - producer of high quality original planting technology articles This website URL: Common pest and disease maps of grape growing, green blind cockroaches prevention and treatment methods and special effects drugs
Urine Test Strips 2K,Urinalysis Strips,Best Urine Test Strips,Urine Analysis Strips Changchun LYZ Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.lyzinstruments.com

step 2: Immediately close the container again.
This protects the remaining test strips from humidity and guarantees strip integrity up to the expiry date indicated.
step 3: Dip the test strip for about 1 second into the fresh urine specimen.
Wipe off any excess urine on the rim of the vessel and blot the edge of the test strip on tissue paper.
step 4: Read the result by comparing the test fields with the color scale on the test pack after 30 to 60 seconds.