Analysis on the Experiment and Scientific Application of the Diagnosis Technology of Rice Leaf Age in Cold Region
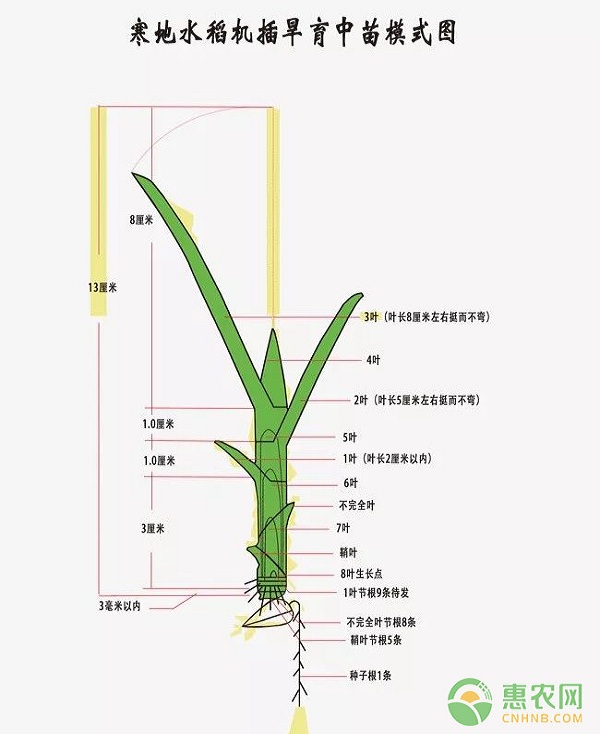
The leaf age diagnosis and cultivation technology of cold rice is the main content of the following series. The leaf age diagnosis and cultivation technique of cold rice is based on the "organ organ extension theory", "leaf age model theory" and "fertilizer effect" of rice, and the new rice cultivation technology developed has been developed for each target yield. According to the results of field diagnosis, the technical system for the regulation of fertilizer, water and plant protection is carried out according to the results of field diagnosis, so that the traditional cultivation techniques of seed, tube and harvest are developed into leaf age diagnosis and prediction. And regulated cultivation technology system. First, the age of the leaf The number of main stems and leaves of different varieties of rice is relatively stable, and each leaf is called a leaf age. A variety of rice, each leaf length is basically fixed. Generally 11 leaf granule varieties rice: The first leaf is about 2 cm long. The second leaf is about 5 cm long. The third leaf is about 8 cm long. The 4th leaf is about 11 cm long. The fifth leaf is about 16 cm long. The sixth leaf is about 21 cm long. The 7th leaf is about 26 cm long. The 8th leaf is about 31 cm long. The 9th leaf is about 36 cm long. The 10th leaf is about 31 cm long. The 11th leaf is about 25 cm long. The second leaf of rice in coldland is the functional leaf of the middle seedling. The focus of the management of Putian is to control the height of the first leaf sheath to no more than 3 cm to ensure that the length of the second leaf (the functional leaf of the seedling) is within the standard range and does not exceed 5 cm. Exceeding is not a strong seedling. This is the diagnostic technique for leaf age of cold rice. Strictly control the time of farming with leaf age, regulate the management of fertilizer and water with the growth of leaf age and fertility, and plan cultivation according to the track of high yield. Only apply it to your rice planting, your rice can be high quality and high yield. Second, according to leaf age for Honda management 1. Tiller period management: The 11 leaf leaves of the 11-leaf variety machine are also called the returning green leaves. The latest initial stage is June 5 and the leaf length is 11 cm. The last leafing stage of the 5 leaves is June 10, the leaf length is about 16 cm, and the leaf color should be thick and the sheath. The latest leaf emergence period of 6 leaves is June 15th, the leaf length is about 21 cm, and the leaf color is darker than the leaf sheath. Water layer management during the tillering period: the flower water is transplanted, the seedling water is poured to the top of the leaf pillow, and the shallow water (3cm) is warmed and promoted. The nutrient element NPK in the base fertilizer has a great influence on tillering. The critical mass of the three elements in the tillering rice seedlings is: 2.5% nitrogen, 0.25% phosphorus, and 0.5% potassium oxide. When the leaf nitrogen content is 3.5%, the tillering is strong, and when the potassium content is 1.5%, the tiller is smooth. The demand for phosphorus in the tillering stage of rice is very large, accounting for about 50% of the total amount of fertilization (base fertilizer). Therefore, if rice is good, the base fertilizer is the key. 2. Management of birth conversion period: After the rice is effectively tillered, it is converted from vegetative growth to reproductive growth and enters the stage of young panicle differentiation. The fertility conversion period is a leaf age period before and after the differentiation of young spikes, that is, the center of the four leaves is the center of the leaf, about 20-40 days before the ear emergence, and the 11 leaf varieties are 7, 8, and 9. Leaf period. The conversion period of fertility is a major turning point in the growth of rice. It is from vegetative growth to reproductive growth, from nitrogen metabolism to carbon metabolism, from stem and leaf growth to spike-grain growth. It is the premise of ensuring safe heading, and it has important significance in the stable yield and high yield of rice in cold regions. Field management during the conversion period of fertility, through the adjustment of nitrogen, strong roots and strong plants, inhibit vegetative growth, promote reproductive growth, control ineffective tillering, adjust the long-term appearance, lay the foundation for the later large-earning and high-grain weight. 3. Water layer management: When the rice reaches the standard of effective tillering, the weather is selected to clear the weather and drain the field to control the occurrence of ineffective tillers. Dry to a large area without water, water in the feet, micro-cracks on the surface. After rehydration, the second drying of the field can be carried out. Through the drying of the field to transport oxygen to the soil, discharge harmful substances, so that the roots are tied down, strong roots and strong rods, laying a good foundation for rice ear development. The latest leafing stage of 7 leaves is June 20th, the leaf length is about 26cm, the leaf color is slightly lighter than the 6 leaf stage, the leaf state is mainly curved leaves, and the stem number reaches 80% of the planned stem number. The last leafing stage of 8 leaves was on June 25th, the leaf length was about 31cm, the leaf color was stable, the leaf state was mainly bent and pretty, and the 11 leaf varieties generally reached the planned number of stems at 7.5 leaf age, and began to differentiate into young ears. . 9 leaves at the latest leafing stage on July 2, the leaf length is about 36 cm. Nitrogen absorption should be regulated during the transition period to promote the growth of the growth center from vegetative growth to reproductive growth, and to enhance physical fitness, increase carbon-nitrogen ratio, control ineffective tillering, and improve plant type and high yield. To improve the plant type is not to have too much nutrient growth in rice. I want to do this. The main reason is that the fertilizer is not used. Some medicines improve plant type and prevent high yield. 4. Management of the fruiting period (1) Fertility process during the fruiting period: From earing to maturity, it is the rice filling period and the rice production period. The 15 days before heading and 25 days after heading are the yield determining period. After flowering, fertilization, grouting (milk ripening, wax ripening, yellow ripening), the rice is finally completed. (2) Fertility process during the fruiting period: After 7-9 days after flowering and fertilization, the ovary is longitudinally elongated, 12-15 days long and wide, and 20-25 days thick. From heading to final maturity, it takes 40-50 days, and the accumulated temperature of activity is about 900 degrees. (3) Fertility and environment during the fruiting period: From the beginning of the ear to the heading for 7 days, in case of low temperature, the heading speed becomes slower, and the heading period is delayed. The flowering period requires higher temperature and sufficient light. At this time, if it is low temperature and continuous rain, it will increase the empty grain rate. The grouting and solidification process is preferably performed at a daily average temperature of 20 degrees or more. The low temperature grouting speed is slow, the daily average temperature drops below 15 degrees, the plant material production capacity stops, the daily average temperature drops below 13 degrees, the photosynthetic products stop running, and the grouting stops, which is the late stage of rice maturity. (4) Blades during the fruiting period: The leaf length and leaf state of the fruiting stage have been shaped, and the normal leaf color is green and not thick. At the heading stage, the number of green leaves of the main stem is not less than 4, and the functional leaves are flag leaves. (5) Irrigation during the fruiting period: The purpose is to root the leaves, prevent leaf senescence, and keep the leaves mature. If the water is flooded for a long time, stopped prematurely, or severely de-fertilized, the speed of leaf aging will increase, which will lead to insufficient material production, increased granules, reduced 1000-grain weight, and reduced production and quality. Intermittent irrigation is required to enter the milk ripening period, that is, 3-5 cm shallow water is poured, naturally dried, and the feet are no longer water replenished, so repeated; the 340 cm shallow water is naturally dried during the ripening period, and the feet are still dry. Replenish water, yellow cooked early drain. 5. Long-earth period management: The time from the differentiation of young spikes to heading is the long-earing stage. The growth point of the long-earing stage is from differentiated leaves to differentiated ears, and the internodes begin to elongate. The sheaths are flat to round, and the roots expand to the surface and underground. The nutrients absorbed from the soil account for 50-60% of the lifetime. There are also many dry substances. In addition to being used as a new organ for growth, some of these substances are stored in the leaf sheath and internodes, and are then transferred to the grain after heading and flowering. Therefore, the long ear stage is not only the period of determining the number of grains, but also the period of determining the seed setting rate and 1000-grain weight. 6. Water layer management: 1. Pre-differentiation of young spikes to the tip of the sword leaves: Intermittent irrigation is mainly used to supply oxygen to the soil, so that the roots are deeper and deeper, and the deep nutrients in the soil are absorbed to avoid root rot, de-fertilization and premature aging. 2. Part of the flag leaf is exposed: water layer is about 10 cm, and it is prepared for defensive obstacles. 3. The distance between the flag leaf pillow and the inverted 2 leaf pillow is between plus and minus 5 cm (meiosis): Within the range of 8-14 days before heading, it is the most sensitive period of low temperature in rice. If there is a low temperature below 17 degrees, the water layer will be deepened to 17 cm or more to prevent the occurrence of obstacle cold damage. Intermittent irrigation will continue in the future. At the latest leafing stage of 10 leaves, on July 9th, the leaf length of 11 leaf varieties is about 30 cm. The color of the leaf sheath should be deep with the leaves, the leaf state is mainly the leaves, the number of stems reaches the highest value, and the ineffective tillers begin to die. During the jointing stage, the base section began to lengthen and the plant height increased rapidly. The first half of the 11 leaf cultivar 10 leaves is a good period for applying panicle fertilizer. The 11 leaf varieties reached 11 leaves on July 15-16, and reached the earing stage on July 25. The tip of the sword leaves is suitable for the closure. Stand on the pool and observe the 4-5 meters in the distance to see the water. The nutrients absorbed from the soil during the long-earing period account for 50-60% of the lifetime. This is a period of good or bad. Whether the fertilizer has stamina or not can be synchronized with rice. Take off without fertilizer. The long ear stage is not only the period in which the number of grains is determined, but also the period in which the seed setting rate and the 1000-grain weight are determined. Therefore, with good base fertilizer, rice can be of high quality and high yield. Do you know about the field trials and applications of the leaf age diagnosis and cultivation techniques of cold rice? Farmers who want to grow cold rice can refer to this article to learn! shockwave therapy,electromagnetic therapy machine,shock therapy machine,light wave therapy machine,electromagnetic wave therapy Shenzhen Guangyang Zhongkang Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.syztreatment.com