Application of liquid nitrogen in heat treatment of materials
1. Liquid nitrogen Liquid nitrogen is nitrogen in a liquid state. Liquid nitrogen can be obtained by special equipment or as a by-product in the process of preparing liquid oxygen. Liquid nitrogen has a very low temperature and a boiling point of -195.8 ° C, which can be used as a cryogenic agent. Liquid nitrogen can also be changed from a liquid to a gaseous state to become nitrogen, which can be passed as a protective gas into a heat treatment furnace. In the air, nitrogen accounts for the largest proportion. Liquid nitrogen is not as flammable and explosive as liquid oxygen. Therefore, liquid nitrogen has the advantages of abundant resources and good safety, and has main applications in heat treatment of materials. Second, the application of liquid nitrogen in vacuum heat treatment Vacuum heat treatment is a relatively advanced heat treatment method being used at home and abroad. In vacuum heat treatment, nitrogen is often indispensable. For example, when the steel piece is heated in a vacuum furnace, if the degree of vacuum is too high, in order to prevent the alloying elements in the workpiece material from volatilizing, an appropriate amount of nitrogen gas is required to be recharged in the furnace to lift the pressure of the trace gas in the furnace. For another example, in the vacuum quenching process of vacuum heating oil quenching, sometimes in order to ensure or improve the cooling ability of the quenching oil, it is necessary to refill the vacuum furnace with sufficient nitrogen before the workpiece is cooled. In high pressure gas quenching, it is necessary to rapidly charge the vacuum furnace with nitrogen gas above one atmosphere. When the steel is vacuum tempered, it is necessary to refill the nitrogen after vacuuming to achieve uniform heating of the protective gas circulation in the furnace, and to achieve rapid cooling after tempering. The nitrogen required for vacuum heat treatment comes from a variety of sources. Since the density of liquid nitrogen is much larger than that of nitrogen, the volume is much smaller than that of nitrogen, which is convenient for transportation and storage, and is also cheaper when supplied in large quantities. Therefore, liquid nitrogen is one of the important sources of nitrogen used in vacuum heat treatment. In foreign countries and Shanghai, China, many manufacturers use larger dedicated storage tanks to store liquid nitrogen transported by liquid nitrogen suppliers, and use nitrogen gas gradually vaporized by liquid nitrogen for vacuum heat treatment. They believe that the use of liquid nitrogen is more economical than using bottled nitrogen or using a nitrogen-producing mechanism. Of course, whether it is calculated by liquid nitrogen or nitrogen in a bottled nitrogen or nitrogen generator is related to the specific conditions of the local gas source conditions and the amount of nitrogen used in the heat treatment plant. The price of liquid nitrogen is not only related to the purity of the liquid, but also related to the amount of one purchase. For example, in the spring and summer of 2003, Xiangtan had an oxygen production and sales of liquid nitrogen. When purchasing 1000L or more, the price was 1 yuan per liter; if it was retail, it was 4 yuan per liter. Third, the application of liquid nitrogen in the material cryogenic treatment Precision measuring tools and some precision devices require stable construction and no deformation during use and storage. Some of these precision gauges and devices made of steel have retained austenite after quenching. If the retained austenite is not eliminated, it is difficult for these gauges and devices to ensure no deformation. An effective method of eliminating this retained austenite is to cold treat it, transform the retained austenite into martensite, and turn it into a stable tempered structure by tempering. Some aluminum alloy parts have the problem of being easily deformed during cutting, long storage, and use. If the deformation problem is not solved, it is easy to cause the scrap rate of the processing or manufacturing to be high, or the quality of the product to be sold is not good. These deformation problems are often related to residual internal stresses generated by raw materials or machining. To solve these deformation problems, it is sometimes necessary to adopt a high-temperature cycle heat treatment method to eliminate residual stress, which includes cold treatment or cryogenic treatment at a low temperature of -130 ° C or lower. In order to eliminate the residual stress after quenching of the aluminum alloy parts, it is sometimes necessary to carry out anti-quenching, that is, the quenched workpiece is subjected to deep cooling, and then the temperature of the workpiece is increased by a faster heating rate to cause the opposite heat to the quenching. stress. There are also special-purpose materials or products that require cold or cryogenic treatment in order to meet dimensional stability and safety requirements for use in low temperature environments. Since the temperature of the liquid nitrogen is -196 ° C and the chemical stability is also good, it can be directly or indirectly used for the above cold treatment. Some shapes are relatively simple, and there is no need to worry about deep cold cracking, aluminum alloy parts or steel parts that do not have to worry about changes in mechanical properties, and can be directly immersed in liquid nitrogen for cryogenic treatment. When it is not possible to directly soak, a volatile gas of liquid nitrogen can be used as a cooling medium. Liquid nitrogen can also be used as a refrigerant to cool the container (low temperature chamber) where the workpiece is placed to the desired cold processing temperature. 4. Mechanical properties of aluminum alloy parts after cryogenic treatment Our company found that the material of the cryotreated aluminum alloy was harder than the material of the same part that was not cold treated. It was later discovered that this phenomenon does not only occur in one part, one kind of material, but is universal. Therefore, we took one of the 2A12 grade T4 aluminum alloy parts for hardness comparison. The results are shown in Table 1. It can be seen from Table 1 that the hardness of the 2A12-T4 aluminum alloy parts after the deep cooling treatment is indeed improved. After 7A04 aluminum alloy is cryogenically treated at -196 ° C, its strength will be significantly improved. It can be seen that the use of liquid nitrogen for cryogenic treatment of aluminum alloy parts at -196 ° C is one of the effective ways to further improve the material strength. 5. Other applications of liquid nitrogen in heat treatment of materials Liquid nitrogen can also be used as a quenching medium for ultra-low temperature quenching. Since the cooling rate of liquid nitrogen is 5 times larger than that of water, the latent heat of vaporization of liquid nitrogen is 1/11 of water, so the workpiece is surrounded by gas immediately after quenching, and the possibility of quenching deformation and quenching is small. After the steel is quenched in liquid nitrogen, the amount of retained austenite is extremely small, which allows it to achieve higher hardness and dimensional stability. However, since liquid nitrogen is easily volatilized, the consumption is large, and the production cost is high, so the application is currently less. In addition, electron microscopy is a large-scale instrument for observing and studying materials and analyzing the quality of heat treatment. Liquid nitrogen is an auxiliary material required for electron microscopy. Sixth, the safety of liquid nitrogen use Although liquid nitrogen is a non-flammable substance, safety must also be taken into account when using, transporting and storing liquid nitrogen. For example, do not touch the liquid nitrogen directly with your hands, and take care to prevent liquid nitrogen from splashing on your body to prevent frostbite; use liquid nitrogen in a ventilated place to prevent nitrogen from suffocating; do not pack liquid nitrogen when shipping liquid nitrogen. Strict, in case of physical explosions and so on. Conclusion Liquid nitrogen is one of the sources of nitrogen required for vacuum heat treatment, and it is a safer and more economical refrigerant for cryogenic treatment of materials. Vacuum heat treatment has broad development prospects; and the cryogenic treatment of materials, whether in stabilizing material organization, preventing product deformation, or exploring further improving material properties, is more worthy of research and application. Therefore, the application of liquid nitrogen in materials and heat treatment also has broad prospects. Industrial Laser Distance Sensor
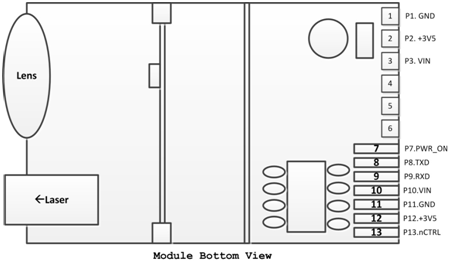
Industrial
Laser Distance Sensor, we also call it secondary development laser distance
module, which support TTL level and CMOS. The laser range sensor can be widely
used in professional surveying, mapping, construction, robots, hunting arrows,
industrial monitoring and automated measurement applications in electricity,
transportation, etc. Our laser distance module supports data communication with
RS232, USB with a simple adapter. The results of laser distance sensor can be
evaluated with Arduino. We are always looking ahead, hoping we can make every
measurement simple in life!
Parameters
of M703A:
Accuracy
±1
mm (0.04 inch)
Measuring
Unit
mm
Measuring
Range (without Reflection)
0.03-60m(150m can customize)
Measuring
Time
0.125~3
seconds
Laser
Class
Class
II
Laser
Type
620-690nm,
<1mW
Size
45*25*12mm (±1 mm)
Weight
About 10g
Voltage
DC2.0~3.3V
Electrical
Level
TTL/CMOS
Frequency
8Hz(20Hz can customize)
Operating
Temperature
0-40 ℃ (32-104 ℉ )
Storage
Temperature
-25~60 ℃ (-13~140 ℉)
Laser Distance RS232,Arduino Distance Module,Laser Module RS232 Chengdu JRT Meter Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.rangesensors.com