Reasonable selection and use of rooting agent for vegetable planting
After vegetable planting, root maintenance can be said to be an important management measure throughout the growth period. For root maintenance, vegetable farmers have the habit of flushing or irrigating rooting agents. However, there are many brands and types of rooting agents. Many vegetable farmers believe that they are called rooting agents anyway, and it is almost the same to use any one. They think that the more rooting agents, the better. In fact, it is not the case. If the rooting agent is not well selected or used, not only can it not play the role of root maintenance, but it will affect the normal growth of the root system. Cause Analysis One is the rooting agents of different brands, the main ingredients are different, such as fungi, amino acids, alginic acid, humic acid, chitin, etc., the ingredients are different, the function is also different. The second is that even if the main ingredients of the rooting agents of the two brands are the same, but the added content is different, the effect produced is also different. The third is that the amount of any fertilizer is fixed. At present, many rooting agents on the market have added some hidden component (not marked on the label), such as naphthaleneacetic acid, indole butyric acid, sodium nitrophenolate and other growth regulators. These growth regulators are hormones. Use (mainly in the early stage), it will cause hormone accumulation and poisoning, causing premature root senility or death. Reasonable choice and use of rooting agent First of all, choose rooting agents according to soil conditions. For example, the shed with many soil-borne diseases can choose the fungal rooting agent, the beneficial bacteria can inhibit the infection and proliferation of harmful bacteria; the shed with nematodes should contain actinomycetes, Paecilomyces lilacinus, and Bacillus Microbial rooting agents, or chitin-based rooting agents, inhibit the occurrence of nematodes in the soil. Secondly, choose rooting agents according to root growth. When the root system encounters unfavorable environmental conditions, such as drought, fertilizer damage, high and low temperature and other environmental stresses, alginic acid rooting agents can be used, which have unique advantages in improving root resistance. There are few roots. If you want to stimulate rooting, promote the growth of root organs and improve fruit quality, you can choose amino acid rooting agents. If the root system grows slowly and grows weakly, in order to supplement the nutrients necessary for root growth, you can choose a vegetative rooting rooting agent, which combines inorganic and organic nutrients to promote the growth and development of the root system. It is necessary to remind vegetable farmers that the rooting agent should be used continuously, and the same kind of rooting agent should be used continuously for more than 3 times. Frequent replacement will affect the effect of fertilizer. Third, do not increase the dosage at will. Rooting agent is not as much as possible. It is recommended that vegetable growers use it according to the recommended dosage on the label. You can choose to apply it during the early or late growth period of the vegetable, when the leaves are good but the root system is weak. This can increase the amount of roots and enhance the absorption capacity of the roots. , The application effect is the most obvious. Disclaimer: Some articles on this website are transferred from the Internet. If the legal rights of a third party are involved, please inform this website for processing. phone Single Packed Yellow Waxy Corn Cob
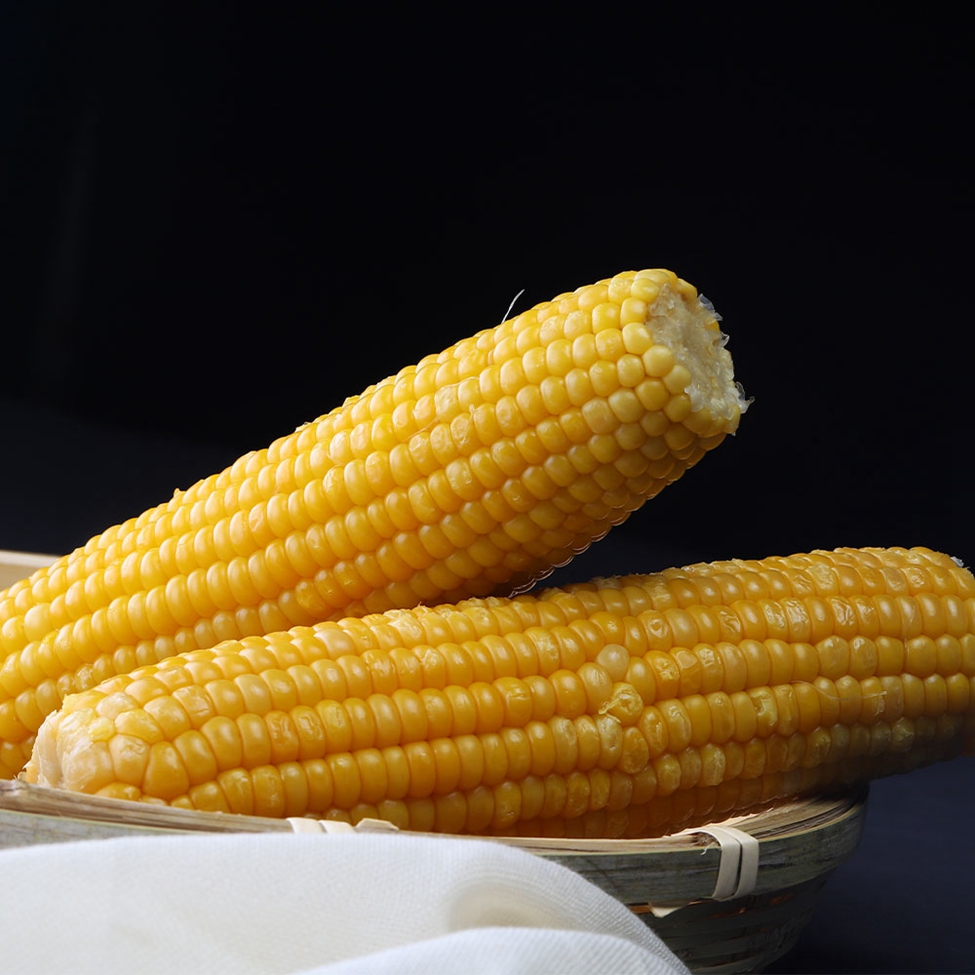
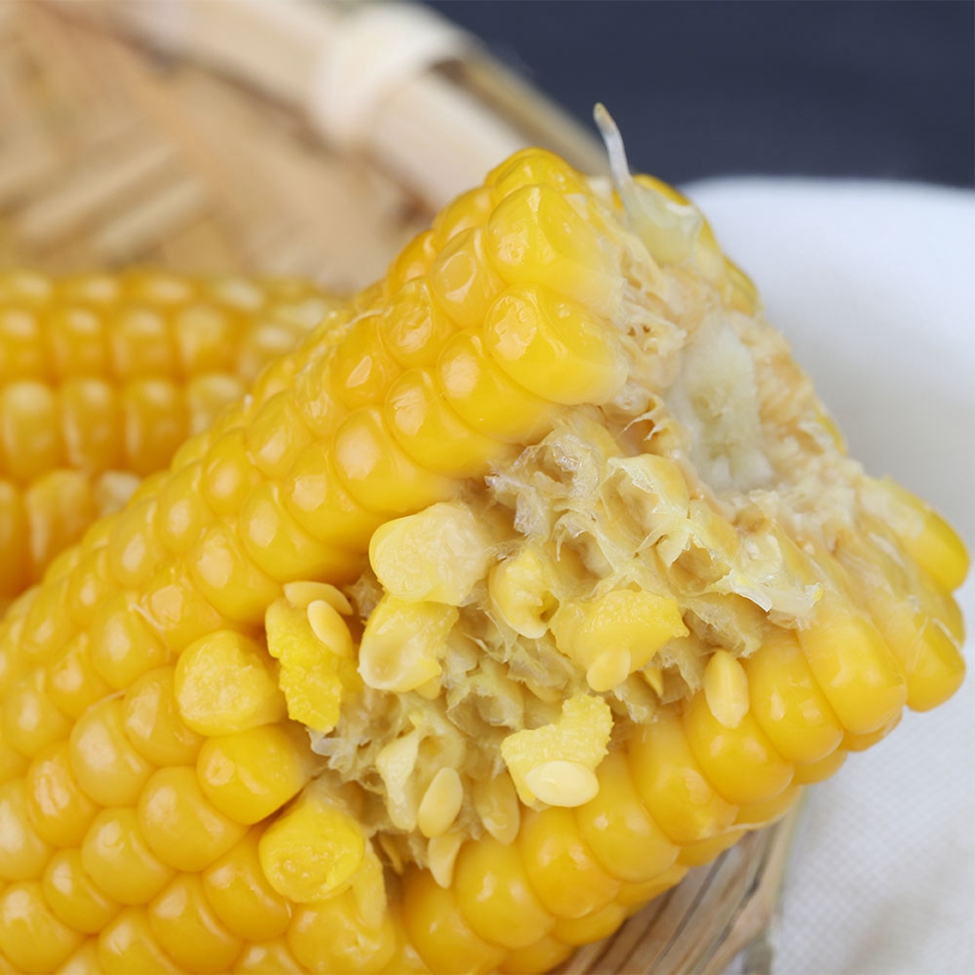
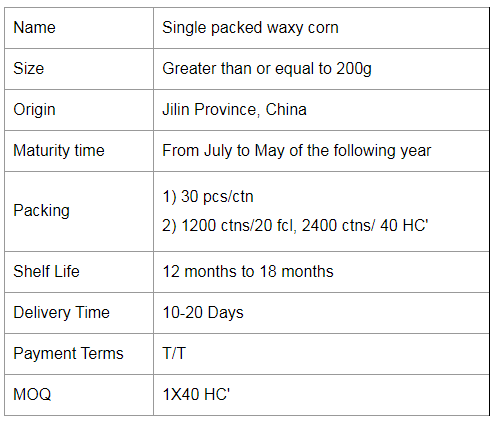
For the most common waxy and sweet corn on the market, waxy corn has a higher nutrient content than regular corn, containing 70-75% starch (and almost all straight-chain starch), more than 10% protein, 4-5% fat and 2% multivitamins, with more grains, VA, VB1 and VB2 in protein than rice, with the highest fat and VB2 content. Yellow maize also contains carotenoids, such as rice and wheat. The molecular weight of waxy maize starch is more than 10 times smaller than that of ordinary maize, and the starch makes glutinous rice sticky and soft, softer than ordinary hard maize. It is more than 20% more digestible to eat than regular maize and it is suitable for people with less than perfect teeth. At the same time, it is not suitable for diabetics because of the very high content of straight-chain starch (a polysaccharide).
Waxy maize is also known as sticky maize. The grain has coarse, waxy endosperm, similar to shiny, glassy (clear) grains such as hard and dent maize. Its chemical and physical characteristics are controlled by a recessive gene, which is located on chromosome 9. 100% of the starch in the endosperm is straight-chain starch.
If you have any further questions about our products, please do not hesitate to contact us. Waxy Corn Cob,Yellow Glutinous Corn,Yellow Waxy Corn Cob,Single Packed Yellow Waxy Corn Cob Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nongsaocorns.com