Meco cooling tower selection formula
Cooling tower selection formula: The function of the cooling tower is to cool a certain amount of water Q from water temperature t1 to t2, or to cool Δt=t1-t2. Therefore, to design a cooling tower of the appropriate size, or to calculate the cooling capacity of an existing cooling tower, we must do the thermal calculation of the cooling tower.
1: The heat dissipation coefficient, the mass coefficient, and the specific heat of the wet air are considered constant throughout the cooling process and do not vary with air temperature and water temperature.
2: In the cooling tower, since the partial pressure of water vapor is small, the influence on the pressure change in the tower is also small, so the pressure in the calculation takes the average atmospheric pressure value.
3: It is considered that the surface temperature of the water film or water droplet is consistent with the internal temperature, that is, the thermal resistance of the water side is not considered.
4: In the heat balance calculation, the amount of evaporated water can be neglected because the amount of evaporated water is not large.
5: The relationship between the saturated water vapor partial pressure and the saturated air and water temperature can be assumed to be linear in the range where the water temperature does not change much.
The thermal calculation methods of the cooling tower include the enthalpy difference method, the wet difference method and the differential pressure method. The most commonly used method is the enthalpy difference method proposed by Michael. The following is a brief introduction to the enthalpy method thermal calculation of the cooling tower.
The enthalpy method proposed by Michael unifies the heat transfer formula that was driven by temperature difference and concentration difference into a heat transfer formula based on coma. In the equation, Michael leads into the Lewis relation and derives the heat dissipation equation based on coma. 


The Chebyshev integration method is recommended by the American Cooling Tower Association (CTI) and is used in the United States and Japan. This integration method is to obtain an integral equation, and obtain a predetermined y value between a and b on the x-axis. The sum of a certain y value is multiplied by a constant value b-a, which is the integral value sought. The points are 0.102673 times, 0.406204 times, 0.593796 times and 0.897327 times of b-a. Find the corresponding y value for its four points. For calculation simplification, one bit after the decimal point is 0.1 times, 0.4 times, 0.6 times and 0.9 times of b-a. Its calculation formula is: 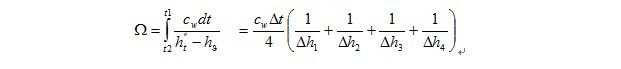
The design of the cooling tower is a trial calculation process, that is, according to the given conditions, the size and internal components of the tower are selected, and then the water temperature t2 is calculated to meet the design requirements. Therefore, the thermal calculation of the cooling tower is to calculate the tower water temperature t2, and also calculate the ventilation and exhaust temperature.