Culture of mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDC)
[Classic BMDC preparation method diagram] DC is the abbreviation of "Dendritic Cells", which is called "dendritic cells" in Chinese. It is named for its many dendritic or pseudo-protrusions. DC was discovered in 1973 by the 2011 Nobel Prize winner and Canadian scientist Ralph M. Steinman [1], and is the most powerful antigen presenting cell (APC) currently discovered. DC has been shown to be the only APC that significantly stimulates the proliferation of naïve T cells, while other types of APCs (such as monocyte macrophages, B cells, etc.) can only stimulate activated or memory T cells. Therefore, DC is the initiator of the body's adaptive T cell immune response and plays an extremely important role in tumor immunity. 1999 - Lutz of the University of Erlangen in Germany developed a method for obtaining a large amount of BMDC. The number of BMDCs available per mouse is 50 times that of the Inaba classic method. 1-3 x 108 DC cells/mouse [8]. This method is widely recognized and used by DC researchers. Excerpt from the literature Son YI, et al. J Immunol Metods. 2002; 262(1-2): 145-57 [9] Note: 1) Generally, a mouse can harvest about 4-5 x 107 bone marrow cells, so at least 40-50 24-well plate wells can be plated. This 50m distance measuring meter is made of two parts: the laser distance outside unit and the sole part laser measure module. Great distance range is from 3cm to 50 meters with ±1.5mm high accuracy. Digital distance measuring device is quick and reliable measure with one hand pushing the button. It is designed for hand helding, very convenient to put in your jacket pocket or trouser pocket. 50M Laser Distance Measurer,Mini Laser Measurer, Laser Measure 50M,50M Laser Distance Meter Chengdu JRT Meter Technology Co., Ltd , http://www.accuracysensor.com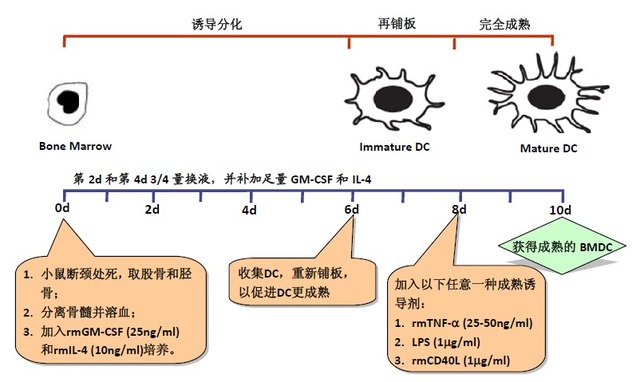
Although DC exists in various tissues in the body, it is rare in content and cannot meet the needs of scientific research and clinical treatment. Therefore, various methods have been tried to culture and amplify DC in vitro. For humans, the most common method is to induce DC production from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). For mice, the most common method is to induce DC from bone marrow cells, namely Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells (BMDC).
In view of the needs of functional analysis and molecular biology research, obtaining higher quantity and higher purity of BMDC is the goal that everyone has been pursuing. This article will share with you the classic preparation method and a large number of preparation methods of BMDC, you can choose according to your own needs. .
In addition, we also have a practical BMDC training operation video (internal communication, non-commercial), because the file is relatively large, if necessary, can be requested to send us through our enterprise QQ (number).
[A brief history of the development of BMDC culture]
1973---Canadian scientist Raplph M. Steinman first identified dendritic cells (Dendritic Cells, DC) from peripheral lymphoid organs (spleen, lymph nodes, and paclitaxer) in mice at Rockefeller University. ) [1]. Steinman also won the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
1992--Inaba, Kyoto University, Japan, successfully injects a large amount of DC from mouse blood and bone marrow cells in vitro with the addition of GM-CSF (granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor) [2] Therefore, Inaba is considered to be the founder of mouse DC in vitro culture, and the Inaba method is called the classical method of mouse BMDC culture.
1. These tasks were completed with the participation of Ralph M. Steinman;
2. Inaba cultured BMDCs are derived from bone marrow in the femur and tibia of mice;
3. Inaba first removes lymphocytes from the bone marrow by antibody + complement to prevent the effects of lymphocytes on BMDC culture;
4. In order to prevent granulocyte interference during the differentiation process, Inaba removes granulocytes as much as possible by gently shaking the plate every 2 days and changing the volume by 3/4 volume;
5. Inaba confirmed that a large number of DC cells could be induced from bone marrow cells by GM-CSF alone for 6-8 days, and the mixed lymphocyte reaction indicated that it was a mature DC cell;
6. This method can obtain 5-7 x 106 DC cells from the bone marrow of a mouse.
In 1994---Romani of the University of Innsbruck in Austria discovered that GM-CSF and IL-4 (interleukin 4) were combined to induce a large amount of PBMC (peripheral blood mononuclear cells) from human blood. DC, and GM-CSF alone is not effective [4]. Later, scientists also applied IL-4 to the culture of mouse BMDC [5,6].
In 1999, the Labeur study at the University of Munster in Germany showed that BMDC induced by GM-CSF alone was induced by immature DC (iDC), GM-CSF and IL-4. The maturity of BMDC is central, and the addition of CD40L or LPS can further induce complete maturation of DC, ie, mature DC (mature DC, mDC) [7].
1. The bone marrow is not pretreated;
2. Replace the cell culture plate with a Petri Dish;
3. The initial plating density of the cells is low, 2 x 105/ml;
4. The cultivation time is extended to 10-12 days;
5. Still only induced by GM-CSF, but reduced after 8 or 10 days;
6. Half-time change on day 6 and day 8, but the aspirated suspension cells were centrifuged and returned to the original plate.
2002 - Son of the University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute (UPCI) has also developed a method for culturing a large number of BMDCs, called the bulk-culture method. This method is available for every mouse. The number of BMDCs is 7-10 times that of Inaba's classic method, ie 3 – 4 x 107 BMDC, and the incubation time is similar to the Inaba classic method, which takes only 7 days [9].
1. After the bone marrow is removed, only hemolysis is performed, and no other treatment is performed;
2. Culture using a 6-well culture plate;
3. Combined induction with GMâ€CSF+ILâ€4 during culture;
4. On the 4th and 7th day of cultivation, add sufficient amounts of GM-CSF and IL-4; 
[Classic BMDC culture method]-Inaba method (improvement) [3,10]
3â„4 Background:
1. The number of BMDCs obtained by the Inaba method is 5-7 x 106 cells/mouse;
2. The original method of Inaba is complicated. It is necessary to remove the lymphocytes in the bone marrow by the antibody + complement method. The subsequent improvement method eliminates this step. In fact, Inaba later said that this step can improve the purity of BMDC. But it will not affect the generation of BMDC, but it can be done [10];
3. Inaba original method only uses GM-CSF to induce the production of BMDC. Although the obtained BMDC has strong stimulating ability in mixed lymphocyte reaction, the maturity of DC is less than the combined induction of GM+IL-4, so later The modified method is mostly induced by GM+IL-4.
3â„4 training steps:
1. Acquisition of mouse bone marrow cells
1.1 Mice (6-10 weeks old) were sacrificed by cervical dislocation. All femurs and tibias were removed by surgery. Scissors and forceps removed the muscle tissue around the bones as much as possible. Note: Do not damage the bone.
1.2 Move the bone to the clean bench and soak it in a sterile dish containing 70% alcohol for 2-5 minutes to disinfect and then wash it twice with sterile PBS;
1.3 Move the bone into another new Petri dish containing PBS, cut off the ends of the bone with scissors, and then take the PBS with a syringe. Insert the needle into the marrow cavity from both ends of the bone and rinse the bone marrow repeatedly into the Petri dish until the bone. Completely white;
1.4 Collect bone marrow suspension and filter small pieces and muscle tissue with 200 mesh nylon mesh;
1.5 The filtrate was centrifuged at 1200 rpm for 5 min, and the supernatant was discarded;
1.6 Add 2 ml of ammonium chloride red blood cell lysate (1x), resuspend the cells, incubate for 3-5 min at room temperature, up to 10 min; preparation of ammonium chloride red blood cell lysate:
Note: 1) Prepare 10x stock solution first, as follows: weigh 82.9 g NH4Cl, 10.0 gKHCO3 and 0.37 g Na2EDTA, dissolve in 1L of distilled water, filter and sterilize by 0.22μm filter, store for 6 months at 4oC; : You can prepare an appropriate amount of 10x stock solution as needed, and each component should be proportionally increased or decreased.
Note: 2) Before use, dilute the 10x stock solution with sterile distilled water 1:9 into 1x working solution. Because ammonium chloride red blood cell lysate has a certain damage effect on bone marrow cells, it is necessary to shorten the hemolysis time.
1.7 Add 10 ml PBS to neutralize the lysate, then centrifuge at 1200 rpm for 5 min, discard the supernatant;
1.8 PBS was washed once, and then the cells were resuspended in RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% FBS, and mouse bone marrow cells were obtained.
2. Induction of differentiation of BMDC
2.1 The mouse bone marrow cells obtained in step 1 were counted and adjusted to a cell concentration of 0.5-1×106/ml with RPMI 1640 complete medium containing 10% FBS;
2.2 Spread into a 24-well culture plate, add 1 ml of cells per well, and add recombinant mouse GM-CSF (20 ng/ml) and IL-4 (10 ng/ml) at 37 ° C in a 5% CO 2 incubator. This is the 0th day of cultivation;
2) The concentration ranges of GM-CSF and IL-4 are 20-50 ng/ml and 10-40 ng/ml, respectively.
2.3 Gently shake the plate every 2 days, then replace the fresh medium with 3/4 volume and make up the cytokines.
Note: 1) The purpose of this step is to remove granulocytes and lymphocytes, due to the growth of granulocytes and lymphocytes;
2) Inaba believes that most of the DC adherence is still strong in the first 4 days of culture, so this method will not lose a lot of DC;
3) If the loss of DC cells is found to be excessive, the method can be changed only on the second day of culture;
4) On the fourth day of culture, it can be seen that the agglomerated DCs are attached to the bottom of the plate, and on the sixth day, many DCs are observed to grow into colonies.
2.4 Between the 5th day and the 8th day, gently blew the culture medium, collect the suspended cells and the cells grown by the adherent cells;
Note: 1) The best collection time is the 6th day of cultivation;
2) The cells at this time are already BMDC, but the maturity is not high, so a subsequent subculture step is required to make it more mature;
3) The 24-well culture plate containing the culture medium (containing DC cells) should be supplemented with fresh RPMI complete medium containing recombinant mouse GM-CSF (20 ng/ml) and IL-4 (10 ng/ml), and continue to culture. So that the BMDC can be collected again later.
Centrifuge at 1200 rpm for 5 min, discard the supernatant;
2.6 Resuspend the cells in RPMI 1640 complete medium containing 10% FBS and count, then adjust the cell concentration to 1 x 106/ml, and add recombinant mouse GM-CSF (20 ng/ml) and IL-4 (10 ng/ml). );
2.7 Cells were plated to 100 mm culture dishes (up to 10 ml per dish) or 6-well culture plates (2 m/well).
2.8 37 ° C, 5% CO2 incubator to continue to culture for 1-2 days;
2.9 Collect suspended cells, which is the more mature BMDC.
Note: 1) Steps 2.5-2.8 are the subculture steps in order to make the BMDC obtained in step 2.4 more mature.
2) A number of spinous adherent cells migrated from the DC cluster within 3 h after re-plating, and after 1 day of culture, these adherent cells were found to be detached from the bottom of the culture plate, and it was found that many typical cells floated in the culture solution. DC.
3. Fully mature BMDC
Note: The BMDC obtained in step 2 is not a fully mature DC. If you want to complete the mature DC, you need LPS, CD40L or TNF-a.
3.1 The BMDC obtained in step 2.4 or 2.9 was centrifuged at 1200 rpm for 5 min, and the supernatant was discarded;
3.2 Resuspend the pellet in RPMI complete medium containing recombinant mouse GM-CSF (20 ng/ml) and IL-4 (10 ng/ml), and adjust the cell concentration to 1x106/ml after counting;
3.3 Add to the 24-well culture plate and add the mature inducer, such as TNF-α (250U/ml), LPS (1μg/ml), or CD40L (1μg/ml); etc.; 3.437°C, 5% CO2 incubator culture 2 day;
3.5 Collecting suspended cells and loosely adherent cells are mature dendritic cells.
[BMDC mass preparation method]-Son method [9]
background:
1. This method can get 30-40x106 DC/mouse in 7 days, which is 7-10 times that of Inaba's classic method. After DC was centrifuged by 14.5% metrizamide, the purity (ie CD11c+/I-Ab+ cells) was 85-95%.
2. The endocytosis ability of DC obtained by this method is weaker than the Inaba classical method, but the amount of secreted IL-12p70 is similar;
3. The DC obtained by this method exhibits a stronger stimulating ability in the mixed lymphocyte reaction than the Inaba classical method;
4. The DC obtained by this method can induce a stronger specific T cell response;
5. The above results suggest that this method can obtain more and more mature BMDC than the classical method.
Training steps:
1. Acquisition of mouse bone marrow cells
See the corresponding steps in the Inaba method (improvement).
2. Mass preparation of BMDC
2.1 The mouse bone marrow cells obtained in step 1 were counted and adjusted to a cell concentration of 2 x 105/ml with RPMI 1640 complete medium containing 10% FBS;
2.2 Spread into 5 well cells in a 6-well culture plate, add recombinant mouse GM-CSF (1000 U/ml) and IL-4 (1000 U/ml), and incubate at 37 ° C, 5% CO2 incubator;
Note: 1) The authors tested the concentration of four cytokines at 125 U/ml, 250 U/ml, 500 U/ml and 1000 U/ml. The lower the concentration, the lower the yield and maturity of BMDC cells, so it is recommended to use 1000. U/ml.
2) The author believes that 1000 U/ml is a very high concentration, which leads to excessive cultivation costs.
2.3 On the 4th day of culture, the recombinant mice were supplemented with recombinant mouse GM-CSF (1000 U/ml) and IL-4 (1000 U/ml); Note: Cytokines were directly added to the culture system without changing the solution. The purpose is to avoid any cell loss to obtain the maximum amount of DC. The author believes that the culture process will inevitably appear yellow in the culture process, if you do not change the liquid and only add cytokines, the cells will soon be due to insufficient nutrition. death. Therefore, I recommend taking half or 3/4 of the culture solution on the 4th and 7th days. After centrifugation, add the fresh medium containing sufficient GM-CSF and IL-4 to resuspend the cell pellet, then put the cells back. To the original board.
2.4 On day 7 of culture, DCs were collected, resuspended in 2-4 ml of RPMI 1640 complete medium, added to an equal volume of 14.5% (w/v) meglumine, and centrifuged at 1200 xg for 20 min at room temperature.
Note: The DC at this time is an incompletely mature BMDC. To further mature, skip to step 3.
2.5 Collect the intermediate layer and wash it 3 times with RPMI 1640 complete medium.
3. The full maturity of BMDC
3.1 The BMDC collected in step 2.4 was re-plated and recombinant mouse GM-CSF (1000 U/ml) and IL-4 (1000 U/ml), and LPS (1-10 μg/ml) were added to the culture system.
3.2 Mature BMDC was obtained by incubating for 2 days at 37 ° C in a 5% CO2 incubator.
[BMDC mass preparation method]-Lutz method [8]
3â„4 Background:
1. The Lutz method is similar to the Son method in that BMDC can be prepared in large quantities, but the Lutz method is more widely used than the Son method. It can be confirmed from the following two aspects:
1) Although the Lutz method was published three years earlier than the Son method (1999 and 2002 respectively), as of December 2015, 633 articles in PubMed cited the Lutz method, while only 24 articles cited the Son method. .
2) There is a communication post on the famous academic social platform in the United States: , ask: Does anyone has a protocol for generating dendritic cells from mouse bone marrow using GM-CSF? Most of the respondents recommended and praise Lutz BMDC culture method.
2. The method can obtain more BMDC, up to 1-3 x 108 mice/mouse, and the purity can reach 90-95%;
3. This method uses a much lower concentration of cytokines than the Son method, which is only 200 U/ml, and it drops to 30-100 U/ml from the 8th day to the 10th day of culture, which can greatly save the reagent cost;
4. The biggest difference between this method and the Inaba classic method and the Son method is the use of a Petri dish instead of a cell culture plate to culture bone marrow cells. Inaba's explanation is that bacterial culture dishes do not easily attach macrophages in the bone marrow, thereby inhibiting the development of macrophages, thereby preventing macrophage inhibition of DC maturation, which may be due to the lower plating density of the method. The main reason for obtaining a large number of BMDCs.
5. However, the culture method takes a long time and takes 10-12 days. On the one hand, it is to obtain more BMDC. On the other hand, most granulocytes and lymphocytes are difficult to survive for so long, so the final acquisition can be improved. Purity of BMDC;
6. This method only uses GM-CSF for induction culture, and the obtained BMDC has both immature and mature DC. To further improve the maturity, LPS or TNF-α should be induced for 1-2 days, among which mature DC cells The content will reach 50-70%.
3â„4 training steps:
1. Acquisition of mouse bone marrow cells
See the corresponding steps in the Inaba method (improvement), taking care to eliminate the hemolysis step.
2. Mass preparation of BMDC
2.1 The mouse bone marrow cells obtained in step 1 were counted and adjusted to a cell concentration of 2 x 105/ml with RPMI 1640 complete medium containing 10% FBS;
2.2 Place 10 ml cells per dish in a 100 mm bacterial culture dish (Petri Dish) and add recombinant mouse GM-CSF (200 U/ml, equivalent to 20 ng/ml for PeproTech's GM-CSF), 37 °C, 5% CO2 incubator culture; Note: The bacteria culture dish is used here instead of the cell culture plate.
2.3 On day 3, add 10 ml of complete culture medium containing 20 ng/ml recombinant mouse GM-CSF to the culture dish;
2.4 On the 6th day and the 8th day, the medium was changed by half, that is, the old culture solution was collected, and after centrifugation, the cell pellet was resuspended in complete culture medium containing 20 ng/ml recombinant mouse GM-CSF, and then the cell suspension was returned. Original dish
2.5 Cells can be collected on day 10, which is BMDC.
Note: 1) The culture can be continued until the 12th day. If the culture is continued, 30-100 U/ml (ie 3 ng-10 ng/ml) of recombinant mouse GM-CSF can be used.
2) Although the longer the culture time, the more mature the cell phenotype (the high expression level of CD11c), the mixed lymphocyte reaction experiment showed that the BMDC harvested on the 8th and 10th day of culture had the strongest stimulating ability, while the cultured The 12-day BMDC stimulation ability was significantly weakened.
3) After 10 days of culture, an average of 9.2 x 106 cells per dish can be harvested.
3. Fully mature BMDC
3.1 Culture day 10 DCs were pipetted and collected to collect suspended cells, centrifuged at 300 xg for 5 min at room temperature;
3.2 Discard the supernatant, resuspend the cell pellet with 10 ml RPMI 1640 complete medium, and then plate it on a 100 mm cell culture plate; Note: instead of using a bacterial culture dish, use a cell culture plate, since BMDC has been formed, In a semi-suspended state, the macrophage precursor remaining in the bone marrow can adhere to the cell culture plate, but it will no longer inhibit the maturation of the DC, but will cause the DC in the suspension because it is attached to the bottom of the plate. The purity is higher.
3.3 Add recombinant mouse GM-CSF (100 U/ml, equivalent to 10 ng/ml from PeproTech) and TNF-α (500 U/ml), or recombinant mouse GM-CSF (100 U/ml, equivalent to PeproTech) 10 ng/ml) and LPS (1 μg/ml);
3.4 37 ° C, 5% CO2 incubator to continue to culture for 1-2 days.
[Qualification of BMDC]
1. Morphological observation: Most of the BMDCs are colony-grown, and the cells have multiple dendritic-like processes, and the mature BMDC is more obvious;
2. Cell phenotypic analysis: Flow cytometry detects the expression of CD11c, CD40, CD80, CD86, MHC class II molecules (IA/IE) on DC cells, BMDC expresses these molecules, and these molecules are fully mature in BMDC. The expression will be further improved.
3. Mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR): BMDC has strong stimulating ability, and the higher the maturity, the stronger the stimulating ability.
Excerpt from the literature Lutz MB, et al. J Immunol Metods. 1999; 223(1): 77-92 [8] 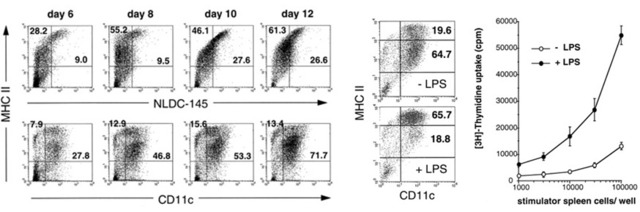
ã€Precautions】
1. Mouse strain and gender:
Most studies have shown that the mouse strain used has little to do with the number and maturity of BMDCs obtained [9], but studies have shown that C57BL/6 mice may be better.
Lutz said that a sufficient number and purity of BMDC can be obtained from mouse strains such as C57BL/10, DBA/2, C3 H/J and 129, but Lutz prefers C57BL/6, ICR and BALB/c in his experiments. In mice, C57BL/6 mice were found to have the highest BMDC production, and BMDCs in ICR mice and C57BL/6 mice were more sensitive to LPS maturation than BALB/c mice [8].
Regarding the sex of mice, Inaba believes that male mice are better because they have larger bones and thus more precursor cells [10], but most scholars prefer to use female mice.
Therefore, the more mice currently used to culture BMDC are female or male C57BL/6 mice.
2. Is GM-CSF used alone or in combination with IL-4?
Inaba classic method and Lutz mass production method can induce a considerable amount of BMDC only by GM-CSF, and also exhibit strong stimulating effect in mixed lymphocyte reaction, but the maturity of these BMDC is not enough. high.
Studies have shown that GM-CSF+IL-4 combined to induce higher expression of MHC class II molecules and costimulatory molecules CD80 and CD86 than GM-CSF alone, suggesting that the former has stronger antigen-presenting ability, and The former showed more effective stimulating ability in mixed lymphocyte reaction [5,7]. It was also found in animal experiments that GM-CSF+IL-4 combined induction of BMDC can produce a protective anti-tumor immune response, while GM- The protective effect of BMDC induced by CSF alone is weak [6], which indicates that the maturity of BMDC induced by GM-CSF+IL-4 is higher than that of BMDC induced by GM-CSF alone.
The Labeur study at the University of Munster in Germany also showed that BMDC induced by GM-CSF alone is immature DC, and the maturity of BMDC induced by GM-CSF and IL-4 is intermediate, adding CD40L or LPS. It can further induce complete maturation of BMDC [7].
Therefore, the author believes that in order to obtain a better function of BMDC, it is best to use GM-CSF and IL-4 to induce bone marrow cells. Moreover, if IL-4 can be added to the Inaba classic method and the Lutz mass production method, a more mature and effective BMDC should be obtained.
3. Selection of mature inducers
LPS, CD40L and TNF-α are common and effective maturation inducers for both human DC and mouse DC. Which one should you choose?
The maturation ability of TNF-a-induced DC is the weakest among the three [7,8]. Both LPS and CD40L are strong inducers of complete maturation of DC in vitro, and the maturation of the induced DCs is similar, but the induced cytokine profile Differences. CD40L-induced mature BMDCs show the strongest immunomodulatory capacity in vivo, including protective and therapeutic tumor immune responses [7].
The concentration used to stimulate DC complete maturation using LPS is generally 1-10 μg/ml, but 0.1 μg/ml already has a very strong effect, but for safety reasons, 1 μg/ml is generally used.
It is important to note for CD40L that the CD40L molecule belongs to the TNF ligand family, which is characterized by its ability to form a trimer. Therefore, it is best to use the recombinant CD40L trimer protein to stimulate DC, which will have a good effect. If CD40L monomer is used to stimulate DC, the maturity is not very high in most cases.
4. Choice of training methods
This article lists the three most commonly used BMDC culture methods to date. We can see more clearly the similarities and differences between the three methods from the table below. I believe that you can make the right judgment according to your needs. 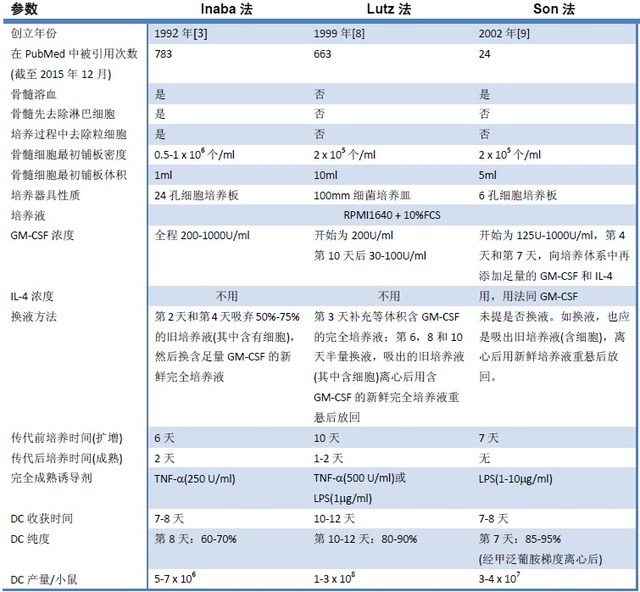
Note: 1. The table was modified and added from the literature [8];
2. The Inaba method here refers to its original method [2], not the improved method in this article.
[BMDC culture reagent recommended] manufacturer product name Product number Product specifications Use concentration PeproTech Recombinant mouse GM-CSF 315-03 5μg/20μg/50μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 25-50ng/ml PeproTech Recombinant mouse IL-4 214-14 5μg/20μg/50μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 10-40ng/ml PeproTech Recombinant mouse TNF-α 315-01A 5μg/20μg/50μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 25-50ng/ml PeproTech Recombinant mouse sCD40L 315-15 5μg/25μg/100μg/250μg/500μg/1mg 1μg/ml
[BMDC identification reagent recommended] manufacturer product name Product number Clone number Fluorescent label Product specifications PeproTech (BioGems) Anti-mouse CD11c fluorescently labeled antibody 3212 N418 FITC/PE/APC/PerCP-Cy5.5 /APC-Cy7/PE-Cy7 25μg/100μg/500μg Anti-mouse CD40 fluorescently labeled antibody 2512 HM40-3 FITC 50μg/100μg/500μg/1000μg Anti-mouse CD80 fluorescently labeled antibody 2912 16-10A1 FITC/PE/APC 25μg/100μg/500μg Anti-mouse CD86 fluorescently labeled antibody 8912 GL-1 FITC/PE/APC/PE-Cy7 25μg/100μg/500μg Anti-mouse MHC class II molecule (IA/IE) fluorescently labeled antibody 86212 M5/114.15.2 FITC/PE/APC/PE-Cy7 25μg/100μg/200μg /500μg
Note: The expression of surface markers for DC identification presents a single peak on the flow chart and in most cases cannot be completely distinguished from the negative peak. In order to avoid the inaccuracy of the results caused by poor compensation adjustment in multicolor analysis, it is recommended to use single label, up to double label for DC surface marker analysis, and must use the same type of control instead of blank cell control to exclude the background. dyeing.
ã€references】
[1] Steinman RM, Cohn ZA. Identification of a novel cell type in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice. I. Morphology, quantitation, tissue distribution. J. Exp. Med. 1973; 137 (5): 1142–62.
[2] Inaba K, Steinman RM, et. al. Identification of proliferating dendritic cell precursors in mouse blood. J. Exp. Med. 1992; 175(5): 1157-67.
[3] Inaba K, Inaba M, et. al. Generation of large numbers of dendritic cells from mouse bone marrow cultures supplemented with granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J. Exp. Med. 1992; 176(6):1693- 702.
[4] Romani N, Gruner S, et. al. Proliferating dendritic cell progenitors in human blood. J. Exp.
Med. 1994; 180(1): 83-93.
[5] Zorina T, Mayordomo JI, et. al. Culture of dendritic cells from murine bone marrow supplemented with GM-CSF and TNF-alpha J. Immunother. 1994; 16(3):247.
[6] Mayordomo JI, Zorina T, et. al. Bone marrow-derived dendritic cells pulsed with synthetic tumour peptides elicit protective and therapeutic antitumour immunity. Nat Med. 1995;1(12):1297-302.
[7] Labeur MS, Roters B, et. al. Generation of tumor immunity by bone marrow-derived dendritic cells correlates with dendritic cell maturation stage. J Immunol. 1999;162(1):168-75.
[8] Lutz MB, Kukutsch N, et. al. An advanced culture method for generating large quantities of highly pure dendritic cells from mouse bone marrow. J Immunol Methods. 1999;223(1):77-92.
[9] Son YI, Egawa S, et. al. A novel bulk-culture method for generating mature dendritic cells from mouse bone marrow cells. J Immunol Methods. 2002; 262(1-2): 145-57.
[10] Inaba, K., Romani, N., et al. Generation of dendritic cells from proliferating mouse bone marrow progenitors. In: Coico, R., Ranz, A., Kruisbeek, AM (Eds.), Current Protocols in Immunology. Wiley, New York. 1998; Unit 3.7.
1>. Easy to Use. It is very easy to learn how to use a Laser Distance Meter, it can measure distance with pressing a single button.
2>. Safety. Using a laser distance meter to measure is much safer than using a measure tape, for users do not need to climb up and down.